Alternating current (AC) power is an electrical current that flows in two directions and switches directions periodically. It is divided into two categories: single-phase and three-phase. Single-phase power is widely used, particularly in residential and small commercial settings.
This article will explore how single-phase power works, how it compares to other forms of AC power, the five advantages of using single-phase power, and how it can be used in residential and commercial applications.
Defining Single-Phase Power
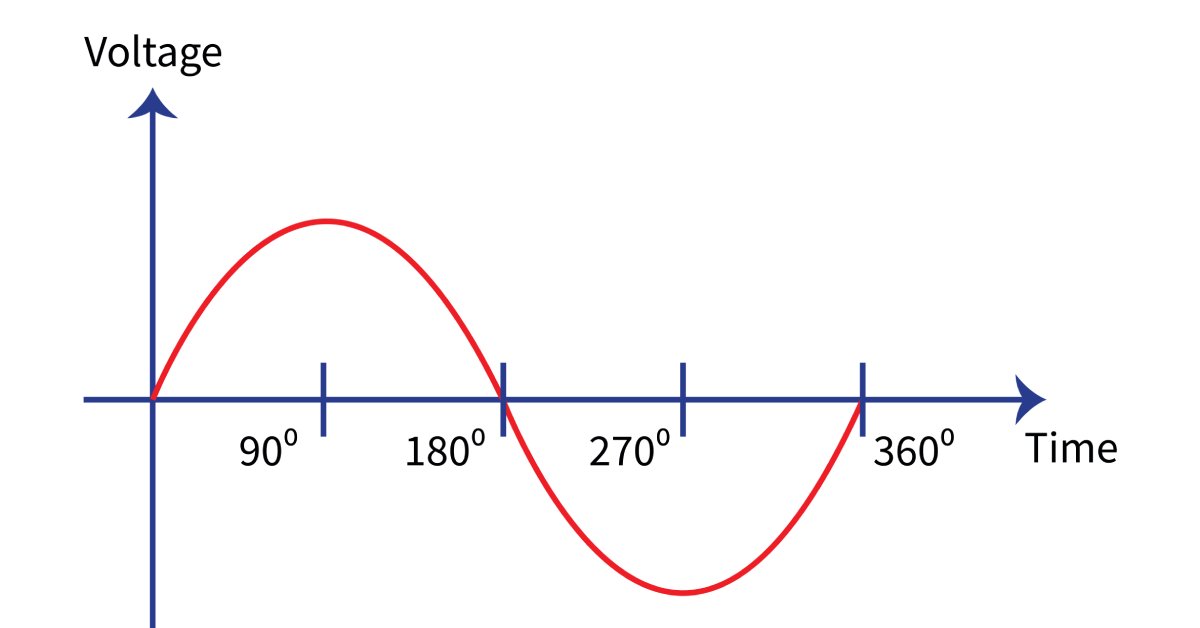
Single-phase power, sometimes called residential voltage, is a type of alternating current that relies on a single sinusoidal wave and uses two wires. The first wire, the phase or live wire, carries a voltage starting at 230 volts and a frequency starting at 50 Hz. The second wire is neutral and serves as the pathway for the current to return to complete the circuit. Single-phase voltage frequently rises and dips, so it does not provide a consistent power supply to the device it is powering.
Comparing Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
Single-phase and three-phase power are often compared because both are widely used electricity distribution methods for homes and businesses. However, there are many distinctions between the two categories of AC power. Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase power is crucial for recognizing the benefits of each system.
Number of Wires
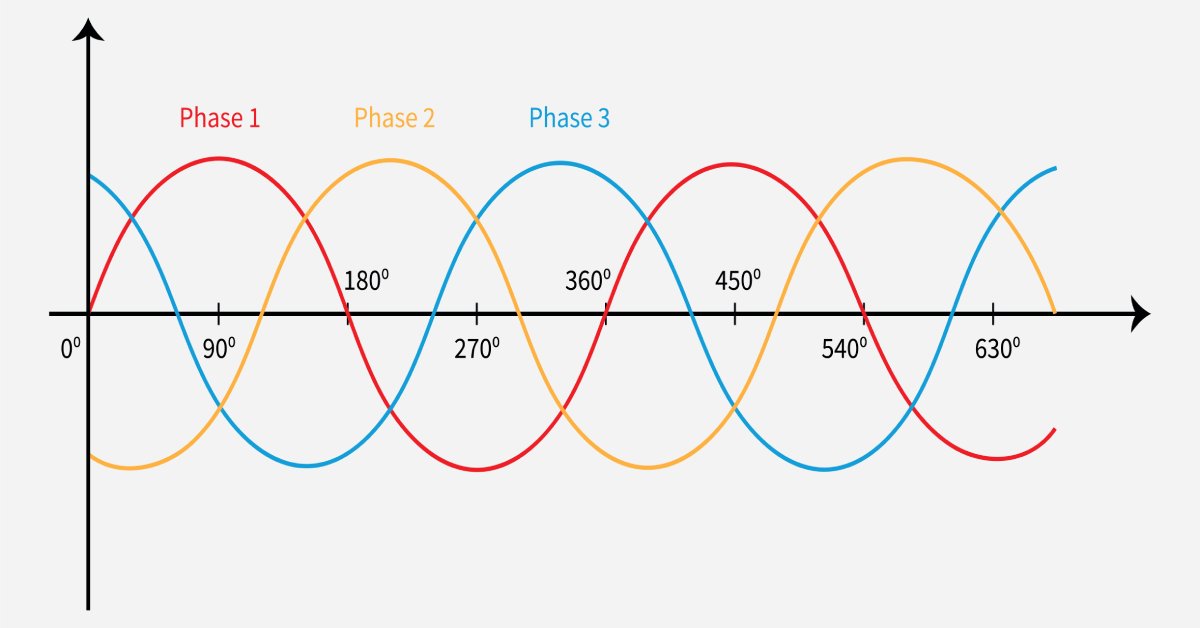
First, single-phase and three-phase power are delivered by different numbers of wires. As we mentioned previously, single-phase power utilizes two wires, while three-phase power uses three or four wires. In three-phase power, a neutral wire is sometimes not present, with the other three wires producing three sinusoidal waves that are offset by 120 degrees. This allows for three-phase power to maintain a more consistent electricity supply.
Voltage Levels
Another significant difference between each power supply is its starting voltage. Single-phase power can reach 230 volts, while three-phase power can withstand 415 volts. This variance in voltage capacity means that single-phase power is typically more suitable for residential and small appliances. In contrast, three-phase power is ideal for heavy-duty industrial equipment because it can handle higher power loads efficiently.
Power Interruptions
Single-phase power systems tend to be more susceptible to interruptions than three-phase systems. In the event of a power supply interruption, single-phase systems may experience a complete power outage, as only one phase is carrying the current.
Conversely, three-phase power systems can often handle interruptions more effectively. Even if one phase goes down, the other two phases can continue to supply power, albeit at reduced efficiency. This redundancy results in a more resilient supply in industrial settings where maintaining continuous power is critical.
Benefits of Single-Phase Power
The advantages of single-phase power present compelling reasons for its widespread use in various contexts. This section will outline the five main benefits of single-phase power supplies.
Cost Effectiveness
One of the most significant advantages of single-phase power is its cost-effectiveness. The installation and maintenance costs associated with single-phase systems are generally lower compared to three-phase systems. This makes it an attractive option for residential and small commercial applications where budget constraints are a concern.
Requires Less Maintenance
Single-phase power systems are simpler in design and construction, which translates to lower maintenance requirements. Technicians find troubleshooting and repairing single-phase systems easier, reducing downtime and keeping operational costs low.
Compact and Lightweight
Another advantage of single-phase power systems is their compact size and lightweight nature. Single-phase equipment typically occupies less space, making it ideal for applications where space is limited. Additionally, the lightweight nature of single-phase equipment simplifies transportation and installation processes.
Less Complex Design
The design of single-phase power systems is less complex than that of three-phase systems. This reduced complexity allows for easier installation and integration into existing infrastructure. Electrical engineers can quickly design and deploy single-phase systems, benefiting time-sensitive projects.
Better Efficiency for Small Outputs
Single-phase power systems are more efficient for loads up to 1,000 watts. They provide sufficient power for most residential and small commercial needs without the excessive complexity and cost of a three-phase system. This efficiency makes single-phase power an attractive option for many low-demand applications.
Drawbacks of Single-Phase Power
Understanding the limitations of single-phase power is important for households and machinery manufacturers to consider when determining the most suitable power system for specific applications. Here are four drawbacks of single-phase power to be aware of.
Lower Power Output
One significant drawback is its lower power output compared to three-phase systems. Single-phase power is not suitable for high-power applications, as it cannot deliver the same level of performance.
Shorter Lifespan
Single-phase power systems tend to have a shorter lifespan due to their inability to provide sufficient torque for motors. This can increase wear and tear on system components, resulting in more frequent replacements and higher long-term costs.
Vulnerable to Power Fluctuations
Single-phase power systems are more susceptible to power fluctuations and interruptions. The lack of redundancy in the system means that any disruption in the single AC waveform can lead to power outages. This vulnerability can be a concern in applications where consistent power supply is critical.
Not Suitable in All Commercial Applications
Due to its lower power output and susceptibility to fluctuations, single-phase power is not suitable for all commercial applications. Industries that require high power output and reliability typically opt for three-phase systems to meet their needs.
Applications for Single-Phase Power
Single-phase power is widely used in residential and light commercial applications. Some common uses include powering household appliances, lighting, and small office equipment. It is also suitable for powering nonindustrial businesses with voltage needs similar to those of households. Lastly, single-phase power can sufficiently run motors and equipment up to five horsepower.
Solid-state frequency converters transform single-phase to three-phase power for low output frequencies and smaller applications. This enables the use of three-phase equipment in locations where only single-phase power is available. These converters are essential for ensuring compatibility and maximizing the utility of single-phase power systems.
Conclusion
Single-phase power offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, lower maintenance requirements, and better efficiency for small outputs. While it has certain limitations, such as lower power output and vulnerability to fluctuations, it remains a valuable option for many applications.
Explore the potential of single-phase power in your projects and consider using frequency converters from Visicomm Industries to expand its applicability. Our products can enhance your industrial facility’s efficiency and performance, reducing downtime and extending machine longevity. Contact us to learn more about the application of frequency converters for your business.